 消息队列(Cloud)
消息队列(Cloud)
友情提示:该文档已过期!!!
考虑到 Spring Cloud Stream 和 Spring Cloud Bus 的学习成本较高,配置较为麻烦,且不够灵活,因此项目已经移除了相关的封装与使用。
😁 建议阅读如下文档,按需使用:
yudao-spring-boot-starter-mq (opens new window) 技术组件,基于 RocketMQ 实现分布式消息队列,支持集群消费、广播消费。
友情提示:我对消息队列不了解,怎么办?
① 项目主要使用 RocketMQ 作为消息队列,所以可以学习下文章:
- 《芋道 Spring Cloud Alibaba 消息队列 RocketMQ 入门》 (opens new window)
- 《芋道 Spring Cloud Alibaba 事件总线 Bus RocketMQ 入门》 (opens new window)
② 如果你想替换使用 Kafka 或者 RabbitMQ,可以参考下文章:
# 1. 集群消费
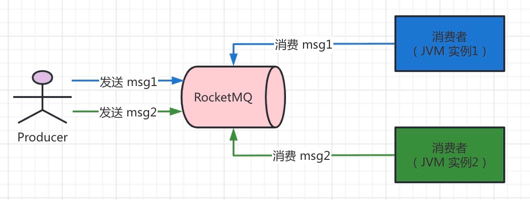
集群消费,是指消息发送到 RocketMQ 时,有且只会被一个消费者(应用 JVM 实例)收到,然后消费成功。如下图所示:
# 1.1 使用场景
集群消费在项目中的使用场景,主要是提供可靠的、可堆积的异步任务的能力。例如说:
- 短信模块,使用它异步 (opens new window)发送短信。
- 邮件模块,使用它异步 (opens new window)发送邮件。
相比 《开发指南 —— 异步任务》 来说,Spring Async 在 JVM 实例重启时,会导致未执行完的任务丢失。而集群消费,因为消息是存储在 RocketMQ 中,所以不会存在该问题。
# 1.2 实战案例
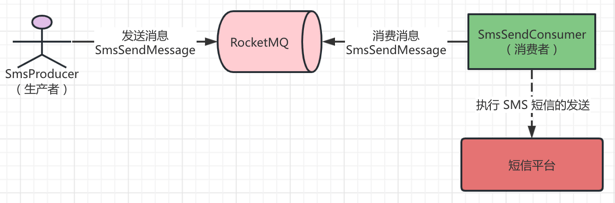
以短信模块异步发送短息为例子,讲解集群消费的使用。
# 1.3.1 引入依赖
在 yudao-module-system-server 模块的 pom.xml (opens new window) 中,引入 yudao-spring-boot-starter-mq 技术组件。如下所示:
<!-- 消息队列相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.iocoder.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>yudao-spring-boot-starter-mq</artifactId>
</dependency>
# 1.3.2 添加配置
① 在 application.yaml (opens new window) 中,添加 spring.cloud.stream 配置。如下所示:
--- #################### MQ 消息队列相关配置 ####################
spring:
cloud:
# Spring Cloud Stream 配置项,对应 BindingServiceProperties 类
stream:
function:
definition: smsSendConsumer;
# Binding 配置项,对应 BindingProperties Map
bindings:
smsSend-out-0:
destination: system_sms_send
smsSendConsumer-in-0:
destination: system_sms_send
group: system_sms_send_consumer_group
# Spring Cloud Stream RocketMQ 配置项
rocketmq:
default: # 默认 bindings 全局配置
producer: # RocketMQ Producer 配置项,对应 RocketMQProducerProperties 类
group: system_producer_group # 生产者分组
send-type: SYNC # 发送模式,SYNC 同步
- 注意,带有
sms关键字的,都是和短信发送相关的配置。
② 在 application-local.yaml (opens new window) 中,添加 spring.cloud.stream 配置。如下所示:
--- #################### MQ 消息队列相关配置 ####################
spring:
cloud:
stream:
rocketmq:
# RocketMQ Binder 配置项,对应 RocketMQBinderConfigurationProperties 类
binder:
name-server: 127.0.0.1:9876 # RocketMQ Namesrv 地址
# 1.3.3 SmsSendMessage
在 yudao-module-system-server 的 mq/message/sms (opens new window) 包下,创建 SmsSendMessage (opens new window) 类,短信发送消息。代码如下:
@Data
public class SmsSendMessage {
/**
* 短信日志编号
*/
@NotNull(message = "短信日志编号不能为空")
private Long logId;
/**
* 手机号
*/
@NotNull(message = "手机号不能为空")
private String mobile;
/**
* 短信渠道编号
*/
@NotNull(message = "短信渠道编号不能为空")
private Long channelId;
/**
* 短信 API 的模板编号
*/
@NotNull(message = "短信 API 的模板编号不能为空")
private String apiTemplateId;
/**
* 短信模板参数
*/
private List<KeyValue<String, Object>> templateParams;
}
# 1.3.4 SmsProducer
① 在 yudao-module-system-server 的 mq/producer/sms (opens new window) 包下,创建 SmsProducer (opens new window) 类,SmsSendMessage 的 Producer 生产者,核心是使用 StreamBridge 发送 SmsSendMessage 消息。代码如下图:
@Component
public class SmsProducer {
@Resource
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
/**
* 发送 {@link SmsSendMessage} 消息
*
* @param logId 短信日志编号
* @param mobile 手机号
* @param channelId 渠道编号
* @param apiTemplateId 短信模板编号
* @param templateParams 短信模板参数
*/
public void sendSmsSendMessage(Long logId, String mobile,
Long channelId, String apiTemplateId, List<KeyValue<String, Object>> templateParams) {
SmsSendMessage message = new SmsSendMessage().setLogId(logId).setMobile(mobile);
message.setChannelId(channelId).setApiTemplateId(apiTemplateId).setTemplateParams(templateParams);
streamBridge.send("smsSend-out-0", message);
}
}
- 注意,这里的
smsSend-out-0和上述的配置文件是对应的噢。
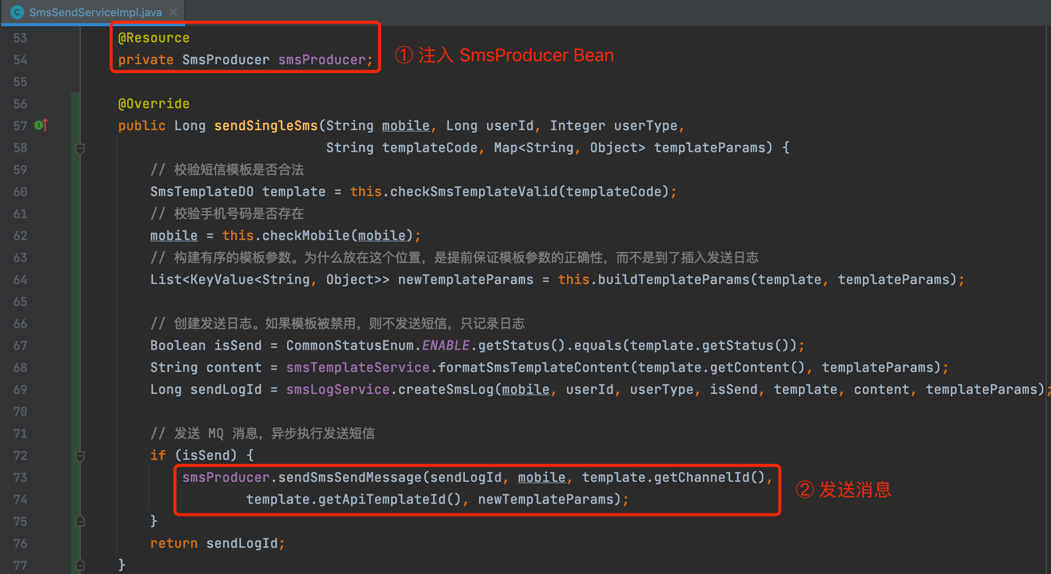
② 发送短信时,需要使用 SmsProducer 发送消息。如下图所示:
# 1.3.4 SmsSendConsumer
在 yudao-module-system-server 的 mq/consumer/sms (opens new window) 包下,创建 SmsSendConsumer (opens new window) 类,SmsSendMessage 的 Consumer 消费者。代码如下图:
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SmsSendConsumer implements Consumer<SmsSendMessage> {
@Resource
private SmsSendService smsSendService;
@Override
public void accept(SmsSendMessage message) {
log.info("[accept][消息内容({})]", message);
smsSendService.doSendSms(message);
}
}
# 2. 广播消费
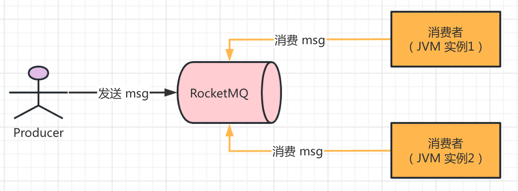
广播消费,是指消息发送到 RocketMQ 时,所有消费者(应用 JVM 实例)收到,然后消费成功。如下图所示:
# 2.1 使用场景
例如说,在应用中,缓存了数据字典等配置表在内存中,可以通过 RocketMQ 广播消费,实现每个应用节点都消费消息,刷新本地内存的缓存。
又例如说,我们基于 WebSocket 实现了 IM 聊天,在我们给用户主动发送消息时,因为我们不知道用户连接的是哪个提供 WebSocket 的应用,所以可以通过 RocketMQ 广播消费。每个应用判断当前用户是否是和自己提供的 WebSocket 服务连接,如果是,则推送消息给用户。
# 2.2 使用方式一:Bus
基于 RocketMQ 的广播消费,可以使用 Spring Cloud Bus 实现。
Spring Cloud Bus 是什么?
Spring Cloud Bus 是 Spring Cloud 的一个子项目,它的作用是将分布式系统的节点与轻量级消息系统链接起来,用于广播状态变化,事件推送等。
它的实现原理是,通过 Spring Cloud Stream 将消息发送到消息代理(如 RabbitMQ、Kafka、RocketMQ),然后通过 Spring Cloud Bus 的事件监听,监听到消息后,进行处理。
以角色的本地缓存刷新为例子,讲解下 Spring Cloud Bus 如何使用 RocketMQ 广播消费。
# 2.2.1 引入依赖
在 yudao-module-system-server 模块的 pom.xml (opens new window) 中,引入 yudao-spring-boot-starter-mq 技术组件。如下所示:
<!-- 消息队列相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.iocoder.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>yudao-spring-boot-starter-mq</artifactId>
</dependency>
# 2.2.2 添加配置
在 application.yaml (opens new window) 中,添加 spring.cloud.bus 配置。如下所示:
spring:
cloud:
# Spring Cloud Bus 配置项,对应 BusProperties 类
bus:
enabled: true # 是否开启,默认为 true
id: ${spring.application.name}:${server.port} # 编号,Spring Cloud Alibaba 建议使用“应用:端口”的格式
destination: springCloudBus # 目标消息队列,默认为 springCloudBus
# 2.2.3 编写代码
参见 《开发指南 —— 本地缓存》 文章的「3. 实时刷新缓存」小节。
# 2.2 使用方式二:Stream
基于 RocketMQ 的广播消费,也可以使用 Spring Cloud Stream 实现。
Spring Cloud Stream 是什么?
Spring Cloud Stream 是 Spring Cloud 的一个子项目,它的作用是为微服务应用构建消息驱动能力。
使用方式,和「1.2 实战案例」小节是一样的,只是需要在 application.yaml 配置文件中,添加 spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.<channelName>.consumer.broadcasting (opens new window) 配置项为 true。
由于项目中暂时使用该方式,文档后续补充。
